Lesson 12 Section 2
HOW TO ROUND OFF A DECIMAL
HOW TO EXPRESS THE QUOTIENT
AS A DECIMAL
Section 1 of this Lesson.
| 4. | How do we round off, or approximate, a decimal to a required number of decimal digits? |
| $6.738 |
|
|
Look at the digit to the right of the required number. If it is a 5 or greater, add 1 to previous digit. If it is less than 5, leave the previous digit unchanged. In either case, drop all the remaining digits. |
|
Example 1. Round off this decimal 7.253896 to three decimal digits.
Answer. 7.253896![]() 7.254
7.254
(The wavy equal sign ![]() means "is approximately equal to.")
means "is approximately equal to.")
To round off to three decimal digits, we must look at the digit in the fourth place. The digit in the fourth place is 8 (greater than 5). Therefore, we add 1 to the previous digit 3.
Example 2. Round off 7.253896 to two decimal digits.
Answer. 7.253896![]() 7.25
7.25
The digit in the third decimal place is 3 (less than 5). Therefore, we leave the digit in the second place (5) unchanged.
Example 3. Round off 7.253896 to the nearest tenth.
Answer. 7.253896![]() 7.3
7.3
To round off to the nearest tenth, means to keep one decimal digit. (To round off to the nearest hundredth would mean to keep two digits; to the nearest thousandth, three; and so on. Lesson 3, Question 5.)
Now, the digit in the second decimal place is 5. Therefore add 1 to the previous digit 2.
Example 4. Round off $6.497014
Answer. This is money. Therefore we must round off to two decimal digits:
$6.497014![]() $6.50
$6.50
The digit in the third decimal place is 7 (greater than 5). Therefore, when we add 1 to 9 of 6.49, we get 6.50
To round off whole numbers, see Lesson 2.
| 5. | How do we express the quotient as a decimal? | ||
|
|
|||
| When there are no more digits in the dividend: | |||
| 1) | Place a decimal point and bring it up to the quotient. | ||
| 2) | Add a 0 onto the remainder, and continue dividing. | ||
| 3) | Add a 0 onto each remainder until the division is exact. If the division will never be exact, round off the quotient to the required number of decimal digits. | ||
Begin,
"4 goes into 32 eight (8) times.
"4 goes into 7 one (1) time with 3 left over.
There are no more digits in the dividend. Therefore, according to the rule: Place a decimal point, bring it up to the quotient, and add a 0 onto the remainder 3:
Continue dividing. Place a 0 after each remainder:
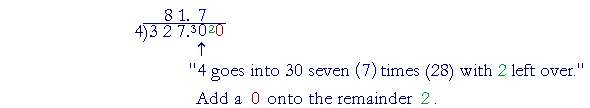

The quotient of 327 ÷ 4, then, may be expressed in three different ways:
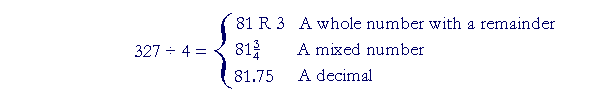
Example 6. Compare the following:
| a) | If it takes 4 yards of material to cover a sofa, how many sofas could you cover with 25 yards? |
| b) | If 4 people go to lunch and the bill is $25, how much does each one pay? |
Solution.
a) We must divide by 4:
"4 goes into 25 six (6) times with 1 left over."
This means that you could cover 6 sofas, and 1 yard of material will remain.
| b) | Again, we must divide by 4, but here we must express the quotient as a decimal -- as money -- and 6 R 1 makes no sense. |
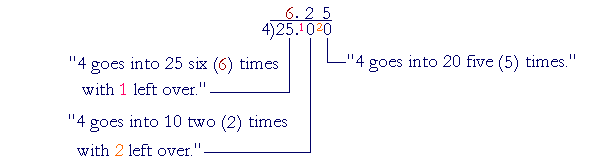
Each person will pay $6.25.
Solution. "6 goes into 12 two (2) times. 6 goes into 7 one (1) time with 1 left over." Place a decimal point, and add a 0 onto the remainder 1:
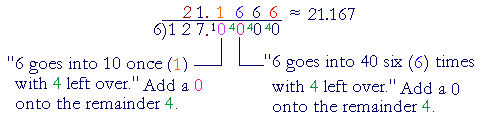
Now the same remainder 4 will be repeated. Therefore this division will never be exact. To round off to three decimal digits, then, we must know the digit in the fourth place -- 6. Therefore, we add 1 to the previous digit; we get 21.167
To round off, we must know one more decimal digit
than is required.
| 6. | How do we proceed when the divdend is less than the divisor? |
| 5 ÷ 8 | |
| Proceed as in the previous case. | |
Example 8. 5 ÷ 8
The dividend 5 is less than the divisor 8. Since 8 is the divisor, write it outside the division box:
"8 goes into 5 zero (0)." Place the decimal point, and add on a 0.
Next, "8 goes into 50 six (6) times (48) with 2 left over."
"8 goes into 20 two (2) times (16) with 4 left over."
"8 goes into 40 five (5) times exactly."
We will see an application of the dividend less than the divisor when we come to changing a fraction to a decimal (Lesson 24). For,
| 5 8 |
= | 5 ÷ 8. |
The horizontal line separating 5 and 8 is the division bar.
Example 9. The following division will not be exact. Round it off to three decimal digits:
1 ÷ 11
Solution. Place 11 outside the box and begin:
"11 goes into 1 zero (0)." Place the decimal point, and add on a 0.
Now 11 does not go into 10. Write 0 in the quotient --
-- and add another 0 onto the dividend.
"11 goes into 100 nine (9) times, with 1 left over."
Write 9 in the quotient, and add a 0 onto the remainder 1.
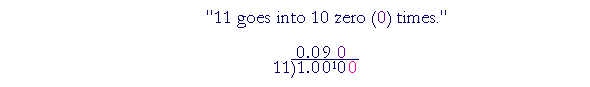
Write 0 in the quotient, and add another 0 to the dividend. Again,
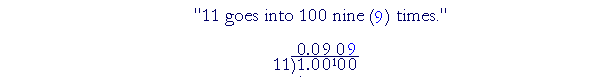
This division will never be exact. We will keep getting 090909. To round it off to three digits, we have calculated the digit in the fourth place. It's 9. Therefore, we will add 1 to the previous digit:
0.0909![]() 0.091
0.091
You sometime see: 1 ÷ 11 = 0.090909... The three dots, called ellipsis, mean: "The decimal for 1 ÷ 11 will never be exact. However, we can approximate it to as many decimal digits as we please by following the pattern 090909."
Calculator problems
Example 10. Patricia pays $66 each year for magazine subscriptions. How much does that cost her each week?
Solution. We must divide $66 by the number of weeks in a year, 52. Press
| 66 | ÷ | 52 | = |
See
| 1.2692307 |
Since this is money, we must round it off to the nearest cent.
1.2692307![]() $1.27
$1.27
It costs Patricia approximately $1.27 each week.
Example 11. A plane flew between New York and Los Angeles, a distance of 2,477 miles, in 4.25 hours. What was its speed in miles per hour?
Solution. Miles "per" hour indicates Miles ÷ hours (Lesson 11). Press
| 2 | 4 | 7 | 7 | ÷ | 4 | . | 2 | 5 | = |
See
| 582.82352 |
This is approximately 582.8 miles per hour.
Example 12. With a calculator, Janet found that 978 ÷ 5 = 195.6.
What actually is the remainder upon dividing 978 by 5?
Answer. 3.
The quotient, 195.6, is what number times 5 will equal 978. (Lesson 11).
| 195.6 × 5 | = | 195 × 5 + .6 × 5 | (Lesson 9) |
| = | 975 + 3. | (Lesson 10) | |
3 is the remainder.
This example illustrates the meaning of a decimal quotient.
It consists of a whole number, 195, plus a decimal fraction, .6. (Lesson 3.)
The digit to the right of the decimal point is not the remainder. .6 is that decimal fraction of the divisor. (Lesson 27.)
Please "turn" the page and do some Problems.
or
Introduction | Home | Table of Contents
Copyright © 2021 Lawrence Spector
Questions or comments?
E-mail: teacher@themathpage.com
