7
TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES
All functions from one function
PLANE TRIGONOMETRY is based on the fact of similar figures. We saw:
Right triangles will be similar if an acute angle of one
is equal to an acute angle of the other.
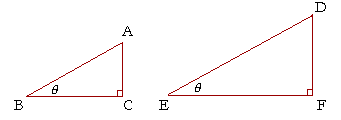
In the right triangles ABC, DEF, if the acute angle at B is equal to the acute angle at E, then those triangles will be similar. Therefore the sides that make the equal angles will be proportional. Whatever ratio CA has to AB, FD will have to DE.
Compare Example 11 here.
A trigonometric Table is a table of ratios of sides. In the Table, each value of sin θ represents the ratio of the opposite side to the hypotenuse -- in every right triangle with that acute angle.
If angle θ is 28°, say, then in every right triangle with a 28° angle, its sides will be in the same ratio. We read in the Table,
sin 28° = .469
This means that in a right triangle having an acute angle of 28°, its opposite side is 469 thousandths of the hypotenuse, which is to say, a little less than half.
It is in this sense that in a right triangle, the trigonometric ratios -- the sine, the cosine, and so on -- are "functions" of the acute angle. They depend only on the acute angle.
Example. Indirect measurement. When we cannot measure things directly, we can use trigonometry.
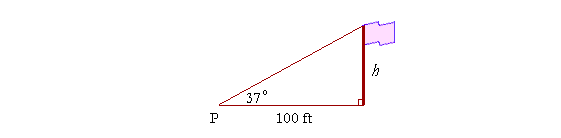
For example, to measure the height h of a flagpole, we could measure a distance of, say, 100 feet from its base. From that point P we could then measure the angle required to sight the top . If that angle, called the angle of elevation, turned out to be 37°, then
| so that | h 100 |
= tan 37° |
| so that | ||
| so that | h | = 100 × tan 37°. |
From the Table,
tan 37° = .754
Therefore, on multiplying by 100,
h = 75.4 feet.
All functions from one function
If we know the value of any one trigonometric function, then -- with the aid of the Pythagorean theorem -- we can find the rest.
Example 1. In a right triangle, sin θ = ![]() Sketch the triangle, place the ratio numbers, and evaluate the remaining functions of θ.
Sketch the triangle, place the ratio numbers, and evaluate the remaining functions of θ.
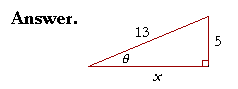
To find the unknown side x, we have
x2 + 52 = 132
x2 = 169 − 25 = 144.
Therefore,
x = ![]() = 12.
= 12.
We can now evaluate all six functions of θ:
| sin θ | = | 5 13 |
csc θ | = | 13 5 |
| cos θ | = | 12 13 |
sec θ | = | 13 12 |
| tan θ | = | 5 12 |
cot θ | = | 12 5 |
Example 2. In a right triangle, sec θ = 4. Sketch the triangle, place the ratio numbers, and evaluate the remaining functions of θ.
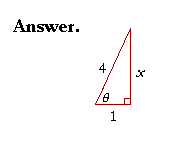
To say that sec θ = 4, is to say that the hypotenuse is
| to the adjacent side in the ratio 4 : 1. (4 = | 4 1 |
) |
To find the unknown side x, we have
| x2 + 12 | = | 42 |
| x2 | = | 16 − 1 = 15. |
Therefore,
x = ![]() .
.
We can now evaluate all six functions of θ:
| sin θ | = | 4 |
csc θ | = | 4 |
|
| cos θ | = | 1 4 |
sec θ | = | 4 | |
| tan θ | = | cot θ | = | 1 |
Problem 1. In a right triangle, cos θ = ![]() . Sketch the triangle and evaluate sin θ.
. Sketch the triangle and evaluate sin θ.
To see the answer, pass your mouse over the colored area.
To cover the answer again, click "Refresh" ("Reload").
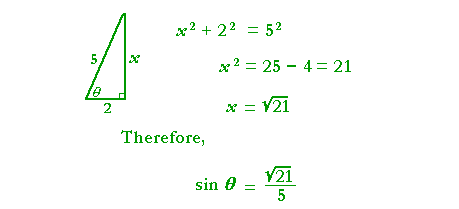
Problem 2. cot θ = ![]() . Sketch the triangle and evaluate
csc θ.
. Sketch the triangle and evaluate
csc θ.
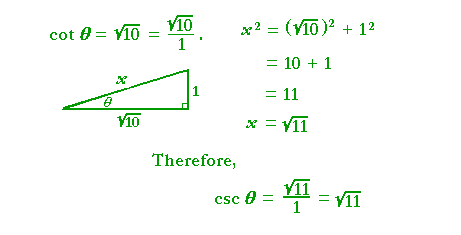
Two angles are called complements of one another if together they equal a right angle.
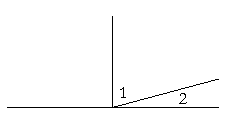
Angles 1 and 2 are complements of one another. Each one completes the other to make a right angle.
In the degree system of measurement, the complement of 60° is 30°.
(Two angles are called supplements of one another if together they equal two right angles. 60° is the supplement of 120°. Their sum is 180°, which is two right angles.)
Problem 3. Name the complement of each angle.
a) 70° 20° b) 20° 70°
c) 45° 45° d) θ 90° − θ
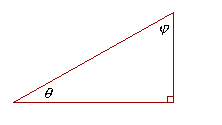
The point about complements is that, in a right triangle, the two acute angles are complementary. For the three angles of the right triangle are together equal to two right angles (Theorem 9); therefore, the two acute angles together will equal one right angle.
Problem 4. In terms of radians, what angle is the complement of an angle θ ?
|
π 2 |
− | θ |
Problem 5. What angle in radians is the complement of each of the following?
| a) | π 6 |
π 3 |
b) | π 8 |
3π 8 |
b) | π 5 |
3π 10 |
c) | π 2 |
0 | d) | 0 | π 2 |
There are three pairs of cofunctions:
The sine and the cosine
The secant and the cosecant
The tangent and the cotangent
Here is the significance of a cofunction:
A function of any angle is equal to the cofunction
of its complement.
This means, for example, that
sin 80° = cos 10°.
The cofunction of the sine is the cosine. And 10° is the complement of 80°.
Problem 4. Answer in terms of cofunctions.
a) cos 5° = sin 85° b) tan 60° = cot 30°
c) csc 12° = sec 78° d) sin (90° − θ) = cos θ
e) cot θ = tan (90° − θ)
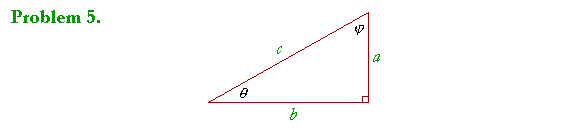
In the figure:
| sin θ = | a c |
cos φ = | a c |
Thus the sine of θ is equal to the cosine of its complement.
| sec θ = | c b |
csc φ = | c b |
The secant of θ is equal to the cosecant of its complement.
| tan θ = | a b |
cot φ = | a b |
The tangent of θ is equal to the cotangent of its complement.
Next Topic: The 30°-60°-90° Triangle
Please make a donation to keep TheMathPage online.
Even $1 will help.
Copyright © 2022 Lawrence Spector
Questions or comments?
E-mail: teacher@themathpage.com